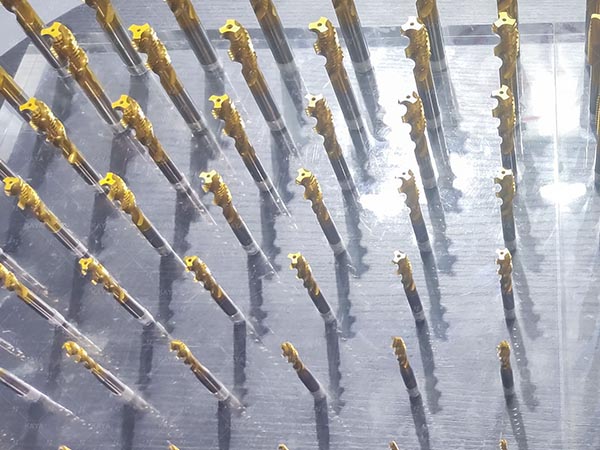
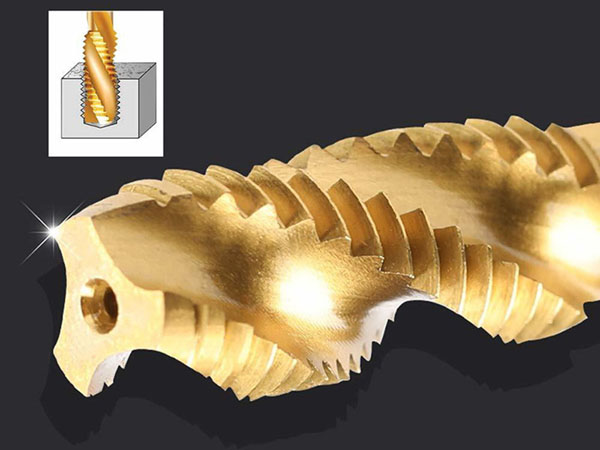
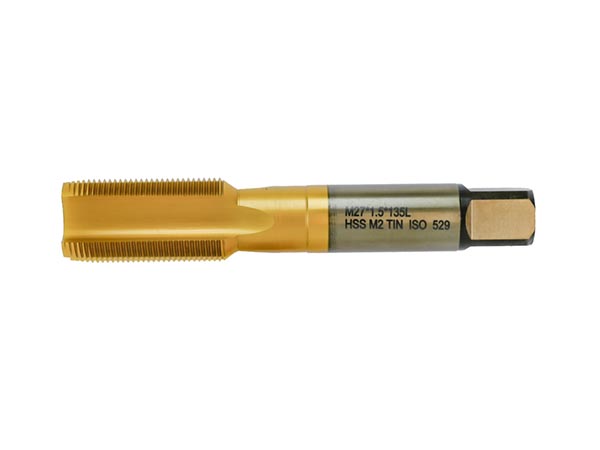
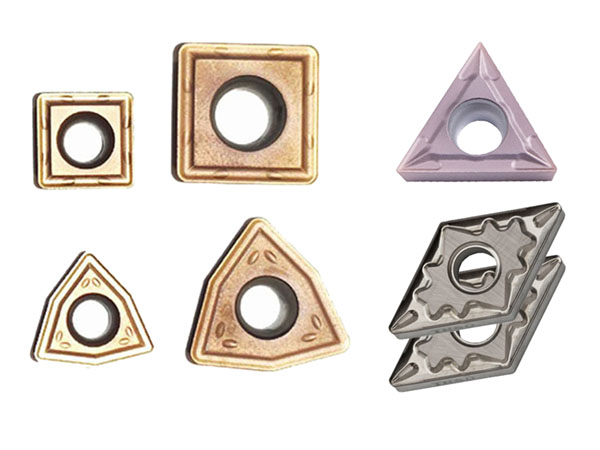
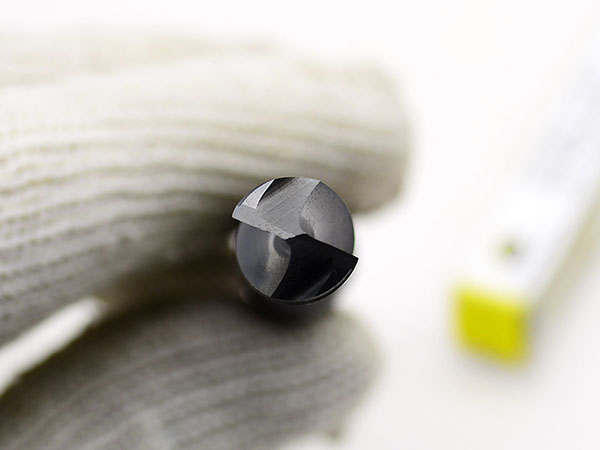
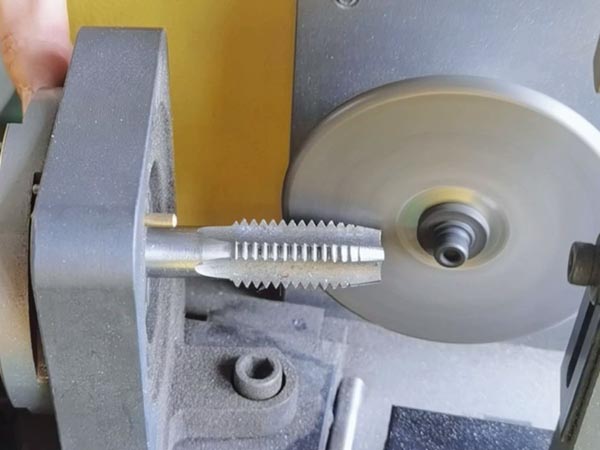
Indexable drill inserts, available in square, triangular, rhombic, and hexagonal shapes, improve stability, chip evacuation, and tool life. Made from carbide, ceramics, and CBN, they suit various industries with future trends focusing on better geometry and design.
View Article