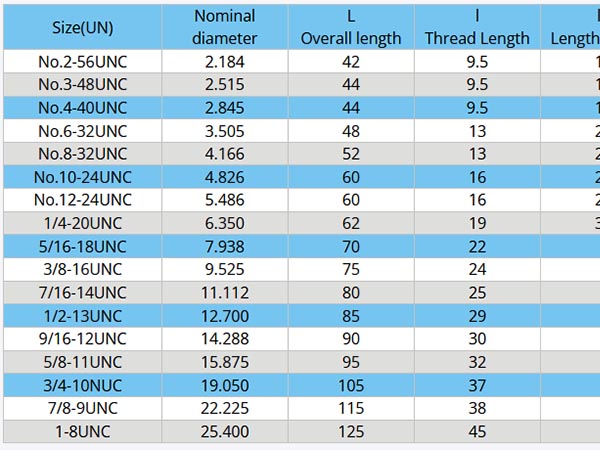
ANSI/UN Thread Standards: Core Parameters & Application Guide
As global manufacturing shifts toward greater precision, American Unified Thread Standards (ANSI/UN) have become essential in mechanical fastening. The dimensional accuracy of these threads directly affects tool performance and equipment reliability. For hardware tool manufacturers in international trade, a deep understanding of thread specifications is not only foundational to meeting client expectations but also critical to enhancing product competitiveness.
This guide draws on production experience to systematically analyze the mechanical behavior, tolerance logic, and machining pitfalls of UNC, UNF, and UNEF threads. It integrates tool selection, material compatibility, and inspection protocols to provide actionable insights for manufacturers looking to align with US and European technical standards and avoid trade disputes caused by misinterpreting thread parameters.
Example: 1/4"-20 UNC
| Type | Features | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| UNC | Coarse pitch, high strength | Steel and cast iron fasteners |
| UNF | Fine pitch, better sealing | Precision instruments, thin-walled parts |
| UNEF | Ultra-fine pitch, anti-loosening | Aerospace, high-vibration environments |

| Thread Type | Rake Angle | Relief Angle | Flute Count |
|---|---|---|---|
| UNC | 8°–10° | 4°–6° | 4 |
| UNF | 6°–8° | 3°–5° | 6 |
| UNEF | 4°–6° | 2°–4° | 8 |
| Workpiece Material | Tool Material Recommendation | Cooling Method | Suggested RPM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Alloy | HSS-E cobalt high-speed steel | Emulsion | 800–1200 RPM |
| Stainless Steel | Powder metallurgy HSS | Oil-based coolant | 300–500 RPM |
| Hardened Steel | Solid carbide | Cryogenic air cooling | 150–300 RPM |
A: Count the number of threads per inch (TPI):
A: Not recommended. Despite both u2025/4/10sing a 55° angle, key differences remain:
Standardized use of American threads is both a technical endeavor and a trade enabler. By analyzing the machining implications of thread angles, pitch, and tolerance grades, manufacturers can optimize tool geometry and coating processes to improve surface quality and prolong tool life. Depending on material hardness and operating conditions, it's crucial to leverage the coarse-thread shear strength and fine-thread anti-loosening properties appropriately. Coupled with inspection methods like three-wire measurement, these practices ensure compliance and traceability.
As green coating and smart sensing technologies evolve, thread machining is moving toward high-efficiency, low-carbon manufacturing. Enterprises are encouraged to build dynamic parameter databases and translate standards into quantifiable production instructions. This approach strengthens technical preparedness to meet the diverse demands of globalized markets.

 We like to do design according to all the customers' requirements, or offer them our new designs. With strong OEM/ODM capabilities, we can fill your sourcing demands.
We like to do design according to all the customers' requirements, or offer them our new designs. With strong OEM/ODM capabilities, we can fill your sourcing demands.