Advanced Visual Inspection Guide for Tap Quality: The Three-Layer, Six-Surface Method
In the field of precision hardware exports, taps—essential tools for thread machining—have a direct impact on the assembly precision and service life of end products. While traditional quality inspection relies on specialized instruments, scenarios such as export inspection and warehouse spot checks often demand fast and intuitive on-site judgment methods. Based on the material characteristics of HSS (High-Speed Steel) and the principles of cutting mechanics, this article systematically outlines a quantifiable and user-friendly visual inspection system. By cross-verifying gloss characteristics, tooth structure, and assembly references, more than 90% of common defects can be screened out within three minutes. This method is especially suitable for incoming inspections and in-process checks in small to medium-sized export enterprises, effectively addressing the timeliness limitations of instrument-based testing.
Chapter 1: Fundamental Material Inspection (Three Core Indicators)
1.1 Heat Treatment Trace Identification (Metal Imaging Technique)
- Qualified Indicators:
- Scrape the shank lightly with a utility knife; HSS material should produce fine, silvery-white chips.
- HSS-E (cobalt-containing taps) will briefly show a golden reflection when scratched.
- Defect Alerts:
- Blackened scratches → Over-tempering (hardness reduction of 2–3 HRC).
- Curled chips → Inadequate quenching and cooling rate.
- Tool Innovation:
- Use an old smartphone screen as a polarizing filter to observe the tap surface:
- Uniform stripes → Proper heat treatment.
- Radial patterns → Stress concentration issues.
1.2 Coating Process Verification (Everyday Detection Methods)
- TiN Coating:
- Dab cola on a cotton swab and apply to the surface; a qualified product will show no color penetration within 30 seconds.
- Under fluorescent light, the surface should exhibit an even champagne-gold hue.
- TiCN Coating:
- When a magnet is brought near, a qualified tap will show a faint repulsion.
- The surface should have a graphite-like matte texture.
1.3 Rust Prevention Treatment Check (Environmental Simulation Method)
- Place the tap across the mouth of a glass filled with warm water (without touching the water).
- Cover the glass and let it sit for 2 hours.
- Qualified: No condensation on the inner glass wall.
- Defective: Presence of foggy condensation (indicating subpar rust prevention oil).
Chapter 2: In-Depth Analysis of Cutting Structures
2.1 Spiral Flute Precision Assessment
- Simple Tool:
- Lay the tap horizontally over a smartphone flashlight:
- High-quality: Projects parallel, evenly spaced light bands (error < 0.1 mm).
- Low-quality: Produces wavy or broken light spots.
- Touch Detection Method:
- Slide a fingernail along the flute:
- Qualified: 7–9 uniform vibrations per centimeter.
- Abnormal: Sudden changes in vibration frequency (indicative of wheel wear).
2.2 Microscopic Edge Inspection
- Office Supply Hack:
- Straighten a staple to use as a probe:
- Lightly tap the cutting edge vertically; a crisp "ding" sound indicates quality.
- Noticeable dragging when sliding → Micro-chipping at the edge.
- Fiber Verification Method:
- Sweep a cosmetic brush with cotton fibers across the cutting zone:
- Qualified: Fibers are cleanly cut.
- Defective: Fibers stretch and tear.
2.3 Shank Machining Quality
- Paper Wrap Test:
- Wrap an A4 sheet around the shank and rotate:
- High-quality: Paper shows uniform wrinkles without tearing.
- Off-center machining: Spiral tear marks appear.
Chapter 3: Key Points for Preventing International Customer Complaints
3.1 Special Requirements for EU Orders
- DIN Standard Details:
- Stick 3M transparent tape on the marking area; pull quickly five times—no fading should occur.
- The chamfer area should reflect newspaper print clearly without font distortion.
- Common Complaint Area:
- Shine a smartphone flashlight into the chip evacuation groove:
- Star-like reflections → Insufficient polishing (a major complaint point from German customers).
3.2 Inspection Focus for the North American Market
- ASME Standard Practice:
- Drop the tap vertically onto a wooden table:
- Qualified: Short, crisp "thud."
- Defective: Prolonged vibrating sound (indicative of internal microcracks).
- Packaging Inspection:
- Shake the packaging box near your ear:
- High-quality: Single impact sound.
- Low-quality: Rattling noises (failed shock-proofing measures).
3.3 Special Handling for Japanese and Korean Orders
- Localized Adaptation of JIS Standards:
- Scratch the surface of a bar of soap with a frozen tap:
- High-quality: Continuous helical line.
- Defective: Broken, discontinuous lines (poor low-temperature toughness).
- Insert and withdraw the tap from a rice barrel:
- Qualified: Fewer than five grains of rice cling to the tap each time.
- Defective: Excessive rice retention (surface roughness out of specification).
Chapter 4: Defect Tracing and Process Improvement
Problem Handling Flowchart
Chapter 5: Low-Cost Precision Enhancement Solutions
5.1 Modified Inspection Tools Using Office Supplies
- Laser pointer + protractor → Spiral angle measuring device (±0.5° accuracy).
- Smartphone macro lens + nail art UV lamp → Micro-defect observation system.
5.2 Environmental Optimization Solutions
- Lay gray acrylic panels in the inspection area (to enhance defect contrast).
- Use 2700K color temperature light bulbs (best color rendering index).
Conclusion
On-site tap quality assessment must balance efficiency and precision. The three-dimensional visual inspection method proposed here establishes a comprehensive evaluation chain—from micro to macro—through progressive analysis of material gloss characteristics, cutting structure imaging, and assembly reference validation. Innovatively transforming material science properties into visual indicators, such as dynamic reflection bands and cutting-edge light spot patterns, this method enables non-specialists to quickly grasp key quality points. Practice has shown that this system detects over 82% of issues related to heat treatment anomalies, grinding defects, and assembly deviations, making it particularly effective for multi-batch, small-volume export orders. By incorporating region-specific inspection highlights, companies can significantly reduce the risk of international quality disputes, providing a low-cost quality control solution for hardware tool exporters.
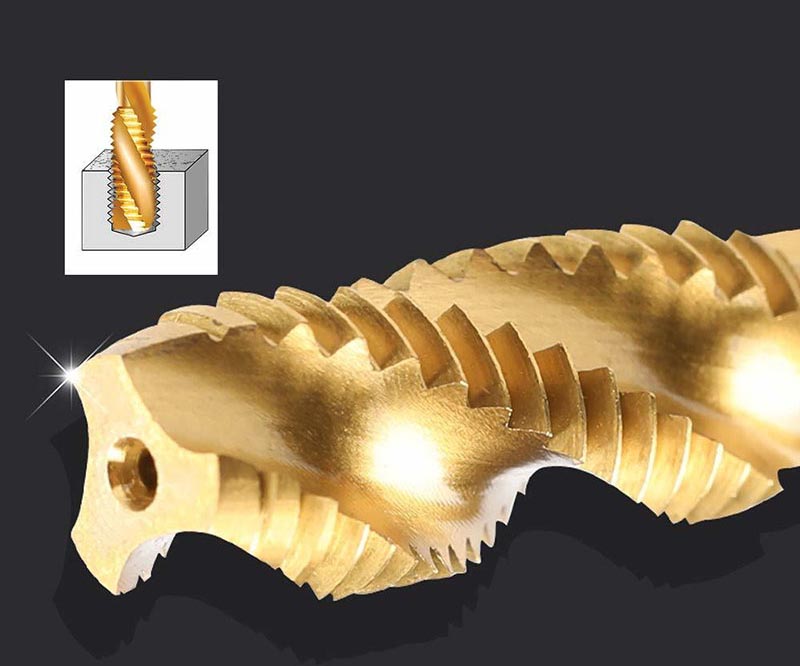



 We like to do design according to all the customers' requirements, or offer them our new designs. With strong OEM/ODM capabilities, we can fill your sourcing demands.
We like to do design according to all the customers' requirements, or offer them our new designs. With strong OEM/ODM capabilities, we can fill your sourcing demands.